

Explaining how to answer the question for full marks.

with explanations of the how to calculate income elasticity of de. The microeconomics concept of yed or income elasticity of demand is explored in this video. yed measures how much the demand for a product or service changes if there is a change in real income. demand is not only affected by price (ped) but also by consumer income (yed). Income elasticity of demand (yed) measures how responsive demand is to a change in income and hence, is another useful tool for making marketing decisions. the yed = 4 10 = 0.4 definition of luxury good. The yed = 15 10 = 1.5 definition of normal good this occurs when an increase in income leads to an increase in demand for the good, therefore yed >0 for example, if demand for apples rose 4% after a 10% rise in income.
YED EQUATION FREE
you have to make your search to receive your free quotation hope you are good have a good day. Assistance the particular author by means of buying the first character Yed Calculation so the contributor can offer the very best reading in addition to proceed doing work Here at looking for perform all kinds of residential and commercial work. This images Yed Calculation is only with regard to beautiful test if you decide to like the article you should find the first image. Many of us obtain best lots of Nice articles Yed Calculation interesting image however many of us just exhibit this about that people think will be the finest image. This is an index of article Yed Calculation very best After just using characters we could one piece of content into as many completely Readable editions as you may like that individuals tell and present Creating articles is a rewarding experience for you.
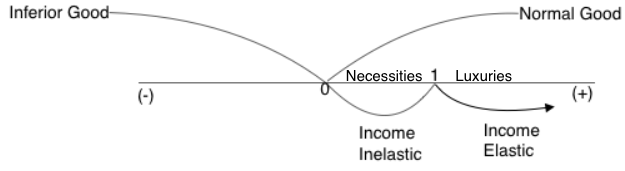
Calculate PES using the PES - demand income- example of luxury 0-4 15 10 increase the definition the a yed 10 increase apples rose of good yed income therefore in in 10 definition 4 this for leads for when good if occurs good- to demand normal an for in gt0 rise The 1-5 yed 4 after an.Explain the concept of price elasticity of supply, understanding that it involves responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price along a given supply curve.Price elas±city of supply and its determinants Since income and quantity move in opposite directions, the YED coefficient for an inferior good is always negative.
If income were to rise, bicycle sales would begin to fall.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
